The Library is pleased to announce that EMBASE.com, the "most comprehensive biomedical and
pharmacological database,” is now freely accessible University-wide at http://www.embase.com. EMBASE.com combines the power of EMBASE and MEDLINE and boasts:
- More than 17 million EMBASE and MEDLINE citations: 10.5 million from EMBASE, 1974- present and 6.5 million non-duplicated MEDLINE records, 1966- present.
- Daily updates, with more than 2,000 records added daily.
- 6,500+ journals from 70 countries, almost 2,000 more journals than covered by EMBASE or MEDLINE individually.
A recent article [1] documents that EMBASE.com provides greater coverage of European and non-English-language publications and broader coverage of pharmaceuticals, psychiatry, toxicology, and alternative medicine than MEDLINE alone. The estimated overlap between MEDLINE and EMBASE is only 30%-50%, and searchers comparing the two databases concluded that relevant information would be missed if only one of the databases was searched.
When it is important for you to know that you have found every relevant article, you are encouraged to search EMBASE.com. As is evident in the "Quick Search" option below, like MEDLINE you can: (1) Explode terms to retrieve all sub-terms and map search terms to preferred terminology; (2) Limit your searches to humans or animals, English articles, and by date; and (3) Truncate keywords using the asterisk (*).
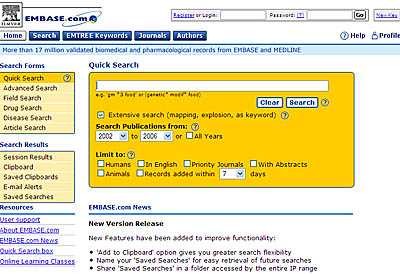
[1] Wong SS-L, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically sound
treatment studies in EMBASE. Journal of the Medical Library Association 2006 94(1):41-7 Jan.
From the "Search Results" page which appears following a search, you can (1) Combine search statements using the Boolean operators AND, OR, and NOT; (2) Save, Delete, E-Mail, Print and Export your search; (3) Sort your research results by relevance or publication year; and (4) Link to the full text of the citation retrieved.
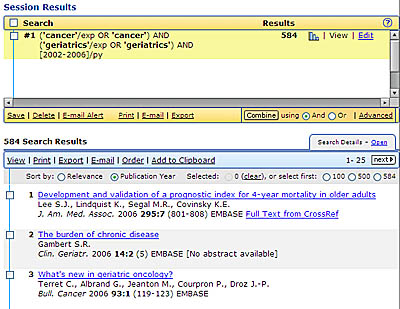
In addition to Quick Search, EMBASE.com offers the following search options:
In the "Advanced Search" and other options, via the "More Limits" link, you can limit EMBASE.com searches to EBM article type, such as Cochrane review, Controlled clinical trial, Meta analysis, Randomized controlled trial and Systematic review. You can also limit to Molecular sequence numbers, Publication type, Discipline, Language, Gender, Age group and Animal study type in the "Advanced Search", "Drug Name", and "Disease Name" search options.
In the "Drug Name" option, you can further limit EMBASE.com searches to Adverse drug reaction; Clinical trial; Drug administration, analysis, combination, comparison, concentration, development, dose, interaction, therapy, and toxicity; Endogenous compounds; Pharmacoeconomics; Pharmacokinetics; and more. You can also limit to one or more of 47 Routes of drug administration.
In the "Disease Name" option, you can further limit EMBASE.com searches to Complication, Congenital disorder, Diagnosis, Disease management, Drug resistance, Drug therapy, Etiology, Epidemiology, Prevention, Radiotherapy, Rehabilitation, Side effect, Surgery and Therapy.
In the "Field Search" option, you can restrict your searches to specific fields, such as Author name and address, CAS registry number, Device manufacturer, Device trade name, Drug manufacturer, Drug trade name, and more. The "Article Search" option facilitates searches for a specific article.
back to top of page
EMBASE.com is also a portal to the Scirus search engine, "the most comprehensive science-specific search engine on the Internet." The Scirus search engine at http://www.scirus.com purports to:
- Search the most comprehensive combination of Web information.
- Pinpoint scientific, scholarly and medical data, and filter out non-scientific sites.
Scirus won the 'Best Specialty Search Engine' award in 2001 and 2002 and the "Best Directory or Search Engine Website Web Award' in 2004.
Whereas Google Scholar, its primary competitor, focuses on access to content in journals, Scirus provides access to
published content, plus 200 million science-related Web pages in pre-selected university, conference, organization,
company with R&D information, government, institutional repository and scientist pages. Scirus "Advanced Search" options include limiting by subject, date range, information type, journal title, author name, etc.
back to top of page
Beginning in January, the following biomedical journals, previously published by Kluwer Academic Publishers, became accessible University-wide on the Springer LINK platform:
AIDS and behavior
Angiogenesis
Biochemical genetics
Biogerontology
Biomedical microdevices
Biotechnology letters
Brain topography
Cancer and metastasis reviews
Cancer causes and control
Cardiovascular engineering
Cell and tissue banking
Cell biology and toxicology
Chromosome research
Clinical and experimental metastasis
Cytotechnology
European journal of epidemiology
Familial cancer
Glycoconjugate journals
Health services & outcomes res. methodology
Heart failure reviews
International journal of cardiovascular imaging
Inter. journal of peptide research and therap.
International urology and nephrology
Investigational new drugs
Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes
Journal of biological physics
Journal of biomedical science
Journal of clinical immunology
Journal of clinical psychol. in med. settings |
|
Journal of computational neuroscience
Journal of computer-aided molecular design
Journal of contemporary psychotherapy
Journal of cross-cultural gerontology
Journal of develop. and physical disabilities
Journal of immigrant health
Journal of medical systems
Journal of molecular histology
Journal of neuro-oncology
Journal of neurocytology
Journal of occupational rehabilitation
Journal of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Journal of structural and functional genomics
Journal of thrombosis and thrombolysis
Maternal and child health journal
Mental health services research
Metabolic brain disease
Molecular and cellular biochemistry
Molecular biology reports
Neurochemical research
Neuropsychology review
Pituitary
Protein journal
Psychiatric quarterly
Quality of life research
Reviews in endocrine & metabolic disorders
Veterinary research communications
Virus genes |
Each title is accessible on the Library's E-Journals A-Z link at https://www.library.miami.edu/calder/index.html by, beginning with the 1997
volumes, and in CALLCAT, the Library's online public access catalog.
back to top of page
In January, the AAMC unveiled MedEdPORTAL, "a new publishing venue through which faculty can
disseminate their educational works," at http://www.aamc.org/mededportal/. Designed to "promote
collaboration and educational scholarship by facilitating the exchange of peer reviewed teaching resources," MedEdPORTAL contains instructional and assessment materials, such as graphics, animations, tutorials, cases, lab manuals, assessment instruments, faculty development materials, computer-based resources, and more." More than 100 virtual patient applications submitted by 71 medical schools are currently accessible. Designed by the Group on Educational Affairs and the AAMC Division of Medical Education, MedEdPORTAL is being implemented in a multi-phase approach. The current phase supports searches by
keyword, discipline, and hot topic and web-based
submission of resources for peer review.
back to top of page
Biomedical Communications is now offering free,
one-on-one tutorials to teach faculty and staff to design high impact scientific posters for presentations and
conferences. The tutorial includes a variety of PowerPoint tools and menus, the basics of page setup, importing objects, and other steps for creating effective poster exhibits. For more information or to make an appointment, please contact Kim Loper at 305-243-6783. Biomedical Communications is conveniently located on the lower level of the Library and is open Monday - Friday, 8:30 a.m. - 5:00 p.m. Information on all aspects of the design and production of posters, business presentations, indoor and outdoor signage, as well as photographic and graphic design, scanning, enlargement, printing, mounting and lamination is
available at https://www.library.miami.edu/calder/index.html/biomed.
back to top of page


